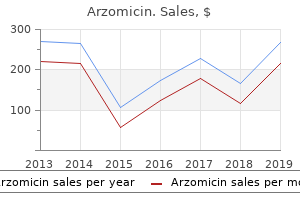
"Buy 100mg arzomicin with visa, virus del nilo".
By: M. Akrabor, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences College of Osteopathic Medicine
Streptolysin O promotes group A Streptococcus immune evasion by accelerated macrophage apoptosis tween 80 antimicrobial order 250mg arzomicin mastercard. Nad glycohydrolase acts as an intracellular toxin to enhance the extracellular survival of group A streptococci bacteria lqp-79 discount 250mg arzomicin otc. Vascular dysfunction and ischemic destruction of tissue in Streptococcus pyogenes infection: the role of streptolysin O-induced platelet/ neutrophil complexes antimicrobial boxers cheap arzomicin 100 mg amex. Role of streptolysin O in a mouse model of invasive group A streptococcal disease antibiotics news buy arzomicin 250mg on-line. Incompetence of neutrophils to invasive group A Streptococcus is attributed to induction of plural virulence factors by dysfunction of a regulator. Reduced virulence of group A streptococcal Tn916 mutants that do not produce streptolysin S. Cytocidal effect of Streptococcus pyogenes on mouse neutrophils in vivo and the critical role of streptolysin S. A two-component regulatory system, CsrR-CsrS, represses expression of three Streptococcus pyogenes virulence factors, hyaluronic acid capsule, streptolysin S, and pyrogenic exotoxin B. Cytotoxic effects of streptolysin O and streptolysin S enhance the virulence of poorly encapsulated group A streptococci. Fc-receptor and M-protein genes of group A streptococci are products of gene duplication. Many group A streptococcal strains express two different immunoglobulin-binding proteins, encoded by closely linked genes: characterization of the proteins expressed by four strains of different M-type. Evasion of phagocytosis through cooperation between two ligandbinding regions in Streptococcus pyogenes M protein. Protective immune response against Streptococcus pyogenes in mice after intranasal vaccination with fibronectin-binding protein SfbI. Nonimmune interaction of the SfbI protein of Streptococcus pyogenes with the immunoglobulin G F(ab=)(2) fragment. A novel, anchorless streptococcal surface protein that binds to human immunoglobulins. IdeS, a highly specific immunoglobulin G (IgG)cleaving enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes, is inhibited by specific IgG antibodies generated during infection. IgG protease Mac/IdeS is not essential for phagocyte resistance or mouse virulence of M1T1 group A Streptococcus. Insight of host immune evasion mediated by two variants of group A Streptococcus Mac protein. EndoS and SpeB from Streptococcus pyogenes inhibit immunoglobulin-mediated opsonophagocytosis. Study of the IgG endoglycosidase EndoS in group A streptococcal phagocyte resistance and virulence. EndoS2 is a unique and conserved enzyme of serotype M49 group A Streptococcus that hydrolyzes N-linked glycans on IgG and alpha1-acid glycoprotein. The SpeB virulence factor of Streptococcus pyogenes, a multifunctional secreted and cell surface molecule with strepadhesin, laminin-binding and cysteine protease activity. Temporal production of streptococcal erythrogenic toxin B (streptococcal cysteine proteinase) in response to nutrient depletion. Substitution of cysteine 192 in a highly conserved Streptococcus pyogenes extracellular cysteine protease (interleukin 1beta convertase) alters proteolytic activity and ablates zymogen processing. Role for a secreted cysteine proteinase in the establishment of host tissue tropism by group A streptococci. Plasminogen is a critical host pathogenicity factor for group A streptococcal infection. A bacterial pathogen co-opts host plasmin to resist killing by cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides. Incorporation of D-alanine into the membrane of Streptococcus pyogenes and its stabilized L-form. Incorporation of D-alanine into lipoteichoic acid and wall teichoic acid in Bacillus subtilis. D-alanylation of teichoic acids promotes group A Streptococcus antimicrobial peptide resistance, neutrophil survival, and epithelial cell invasion. Inactivation of DltA modulates virulence factor expression in Streptococcus pyogenes.
Fertuck antibiotic resistance occurs quickly because arzomicin 250 mg visa, PhD antibiotics for uti or kidney infection cheap 250mg arzomicin visa, City University of New York (C-3) the Effects of the Big Five Personality Traits antibiotics for acne names buy 500 mg arzomicin visa, Gratitude bacteria h pylori espanol purchase arzomicin 250mg visa, Hope, and Self-Esteem on Happiness. Oliveira, PhD, Universidade Lusofona, Lisboa, Portugal (C-4) Social Identity Framing: Social Context and Sources Change Message Processing. Monika Prusik, PhD, Maria Grzegorzewska University, Warsaw, Mazowieckie, Poland; and Maria Lewicka, PhD, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Torun, Poland (C-9) Relationship Among Religions, Social Attitudes Toward Minorities, and Critical Consciousness. Gentile, PhD, Iowa State University (D-2) Social and Emotional Skills As a Mediator Between Ethnic Identity and Ethnocultural Empathy. Boardman, PhD, and Klint Hobbs, PhD, Brigham Young University (D-5) Implicit Math-Gender Stereotypes in Sexist Societies. Hansen, PhD, City University of New York at York College (D-7) Preferring Irreligious Conservative Countries Is Associated With Oppression and Intolerance. Hansen, PhD, City University of New York at York College (D-9) Media Focus on Human Trafficking in the United States and Germany. Post Campus (D-10) Locked Up, Then Locked Out: Exoffender Gender and Employer Attitudes. Kerig, PhD, University of Utah (E-3) Utilizing Exploratory Factor Analysis to Create a Culturally Competent Risk Assessment. Taylor, PhD, University of Utah (E-4) Behavioral, Demographic, and Proximal Risk Factors for Pathological Gambling in the Military Community. Yihong Wang, Beijing Xinye Culture and Arts Limited Company, China (E-8) Switched at Birth and Media Internalization Among Deaf Women. Richardson, PhD, Penn State University Park (E-10) the Need for New Attention to the Bullying of Gay and Bisexual Male Youth. French, PhD, Washington State University; and Brian Hand, PhD, University of Iowa (G-9) Self-Explanation and Imagery: Tools for Learning. Johnson, PhD, University of Cincinnati (H-3) Language Domains Differently Predict Mathematics Performance in Young Children. Emotions Experienced and Perceived in Representational and Nonrepresentational Art Gregory J. Creativity of Songs and Stories Prompted by a Picture: Effects of Musical Expertise Pablo P. Tinio, PhD, and Paul Locher, PhD, Montclair State University; and Elizabeth Krupinski, PhD, Emory University. Heddy, PhD, University of Oklahoma (G-3) the Role of Social Emotions and Coregulation of Learning During Complex Math Problem Solving. Michael Cook, PhD, Virginia Tech (H-5) Positive Affect of the Virtual ``Wild' in Learning a Foreign Language. Cimetta, PhD, University of Arizona (H-11) Measuring Relational Reasoning Among Chinese Elementary and Middle School Students. Slavin, PhD, Johns Hopkins University (I-4) Developing Argument Skills Through Agreeing and Disagreeing Peer Interaction. Flora Matos, PhD, Teachers College, Columbia University (I-5) Relations Among Social Goals, Emotions, Engagement: Roles of Interdependent Self-Construals. Vogel, PhD, Iowa State University (I-9) A Tale of Two Interventions: the Effects of Self-Compassion and Affirmation on Distress and Stigma. Vogel, PhD, Iowa State University (I-10) Body Image and Self-Compassion: A Qualitative Analysis of Intervention Responsiveness. Keitel, PhD, Fordham University; and Rachel Marsh, PhD, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York (I-12) Examining If Feedback Can Influence Racial Biases Demonstrated in Clinical Judgment for Trainees. Imel, PhD, University of Utah (J-4) Formal and Informal Help-Seeking Intentions and Utilization Among Substance-Using College Students.
In human pregnancy infection 7 days to die discount 100mg arzomicin overnight delivery, increased insulin secretion is associated with morphologic changes in the pancreas antimicrobial 2 cheap 100mg arzomicin visa, including marked -cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia [28] antibiotics ear drops generic 500mg arzomicin with amex. Pregnancy-related maternal insulin resistance benefits fetal growth antibiotic prescribing guidelines cheap 250 mg arzomicin free shipping, because a rise in post-prandial glucose concentration aids glucose transfer to the fetus, a process termed "facilitated anabolism" [31]. Maternal to fetal glucose transfer in the fasting state is enhanced by maternal lipolysis, which occurs in late pregnancy, with free fatty acids becoming the main maternal fuel substrate and diversion of glucose to the fetus. These metabolic changes facilitate the transfer of glucose and amino acids to the fetus. An increase in hepatic glucose output in late pregnancy, owing to hepatic insulin resistance, ensures that maternal glucose is available to the fetus between meals [26]. Transgenic mice that overexpress human placental growth hormone develop severe peripheral insulin resistance, similar to that found in the third trimester of pregnancy, confirming its importance in the insulin resistance of late pregnancy. Plasma leptin doubles in pregnancy, being produced by both maternal adipose stores and the fetoplacental unit but its role in maternal metabolism is uncertain [45]. Further demands on their -cells often results in a treatment escalation from diet to insulin early in pregnancy to maintain glycemic control. High doses of insulin are frequently needed, and it is not unusual for women to require in excess of 300 U/day by late pregnancy, only to be well controlled with no insulin postpartum [50]. Both obesity and increasing weight gain postpartum are major determinants for the development of diabetes [65]. Effect of maternal diabetes on pregnancy Maternal diabetes influences all aspects of pregnancy, from fertility through to birth, and subsequent health of the child and adult. While hyperglycemia is the most obvious metabolic abnormality of a diabetic pregnancy, other metabolic abnormalities can also influence outcome as implied by the term "fuel-mediated teratogenesis" [31]. In addition, diabetic complications, such as microalbuminuria, can influence the risk of obstetric complications, including hypertension and pre-eclampsia. Insulin receptors are highly expressed in the trophoblast and endothelial cells of the placenta and maternal and fetal insulin regulates nutrient transfer between the maternal and fetal circulation [70]. Placental insulin-binding capacity is increased in macrosomic diabetic pregnancies compared to nondiabetic placentas [71]. Fertility Before the availability of insulin, most women with diabetes died within 2 years of diagnosis, and pregnancy was rare. In the 1920s, only one diabetic-related pregnancy was recorded in 35 000 deliveries at two London teaching hospitals [72]. Among those women who became pregnant approximately half of mothers and babies died [73]. These women have insufficient -cell capacity to maintain euglycemia and are typically obese and insulin-resistant before pregnancy. They have lower insulin responses to oral glucose at 30 and 60 minutes than glucose-tolerant control subjects [53,54]. Differences in insulin sensitivity between glucose intolerant and glucose-tolerant women are less marked as pregnancy progresses [26]. Even lesser degrees of glucose intolerance are accompanied by abnormal glycerol and free fatty acid metabolism [55] and higher circulating pro-insulin concentrations [56]. Early fetal loss in non-diabetic pregnancies is often attributable to lethal chromosomal abnormalities and once a viable fetus is confirmed by ultrasound at around 8 weeks, the miscarriage rate falls and continues to fall with increasing gestational age [87,88]. Diabetic pregnancies are not at increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities but non-viable congenital malformations are more common than in non-diabetic pregnancies.
Order 100mg arzomicin free shipping. GCSE Biology Revision: Antibiotic resistance.
© 2020 Vista Ridge Academy | Powered by Blue Note Web Design