"Cheap 20 mg olmesartan with visa, arteria rectalis inferior".
By: F. Sobota, M.B.A., M.D.
Co-Director, University of Alabama School of Medicine
Studies in young adult Zn-deficient mice have shown greatly depressed responses to both T-lymphocyte-dependent and T-lymphocyte-independent antigens blood pressure chart in uk generic olmesartan 10 mg line. Both primary and secondary antibody responses have been reported to decrease in Zndeficient mice blood pressure medication dehydration generic olmesartan 20mg with amex. A decline in in vivo-generated cytotoxic Tkiller activity to allogenic tumour cells in Zn-deficient mice has been observed blood pressure questions and answers order olmesartan 40 mg with amex. All these effects of Zn deficiency on immune functions in mice can be reversed with Zn supplementation blood pressure average purchase 10 mg olmesartan fast delivery. Mice maintained on a Zndeficient diet for as little as 2 weeks develop severe impairment of their ability to generate a cytotoxic response when challenged with tumour cells. Moreover, challenging zincdeficient mice with sub-acute levels of infectious agents such as Trypanosoma cruzi or nematodes results in death due to an impaired defence system (Fraker et al, 1982). Therefore, these studies have been helpful to clarify how essential zinc is to the integrity of the immune system. Zinc deficiency in humans In humans, several abnormalities of cellular immunity have been observed. Acrodermatitis, a genetic disorder of Zn Zinc and immune function M Dardenne S21 malabsorption, is characterized by mucocutaneous lesions, diarrhoea, failure to thrive, and frequent severe infections with fungi, viruses and bacteria. Less severe cellular immune defects have been reported in patients who become Zn-deficient while receiving total parenteral nutrition. Similar immunological abnormalities have also been observed in human experimental model subjects in whom mild Zn deficiency has been induced by dietary means. These studies show that even mild zinc deficiency in humans may be accompanied by an imbalance in Th1 cell and Th2 cell functions, resulting in an unregulated resistance to infection. In most studies regarding elderly subjects, plasma zinc has reported to be normal or slightly decreased (Kaplan et al, 1988). However, some authors point out deficient zinc levels in lymphocytes and granulocytes as compared to younger control subjects. Effect of excessive zinc intake Controversial results have been obtained regarding the effects of elevated zinc intake on the immune system. In experimental models, high-zinc diets have been shown to reinforce immune functions above basal levels such as: increased mitogenic responses, increased macrophages or Tlymphocyte functions; this outcome has been described in rats or mice. However, other studies on neonates have demonstrated the adverse effects of zinc excess (Shankar & Prasad, 1998). Other studies suggest that very high intakes by children and adults can induce anaemia, growth retardation, copper deficiency and immunosuppression. Thus, excessive zinc supplementation in healthy people could have deleterious effects on the immune system, and caution must be exercised when taking large zinc supplements for prolonged periods of time. However, mechanisms underlying the relationship between zinc and immunity are still open to speculation. Several hypotheses can be made: (1) Zinc is an essential factor for the activity of many enzymes - it is known to form part of more than 300 metalloenzymes which cannot function in its absence. In addition, zinc forms the active enzymatic sites of many metalloproteases (Frieke, 2000). This has been clearly shown for thymulin, a nonapeptidic hormone (Glu-Ala-Lys-Ser-Gln-Gly-Gly-SerAsn) secreted by thymic epithelial cells, and requiring the presence of zinc for its biological activity. Zinc is bound to thymulin in a 1:1 stoichiometry via the side chains of asparagine and the hydroxyl groups of the two serines. Thymulin activity, in vitro and in vivo, in both animals and humans, is dependent on plasma zinc European Journal of Clinical Nutrition Effect of foetal zinc deficiency Gestational zinc deficiency in mice has short- and long-term deleterious effects on their offspring (Beach et al, 1982). Significant reductions are seen in lymphoid organ size and immunoglobulin concentrations in offspring from marginally zinc-deficient mice. Other murine studies have shown that several immunodeficiencies seen at birth persist into adulthood even when groups are fed a diet containing normal amounts of zinc after weaning. In humans, intra-uterine growth retardation linked to maternal zinc deficiency, induces persistent cellular immune deficiency (Meadows et al, 1981).
Carbon Disulfide Mild poisonings by carbon disulfide inhalation may be managed best by no more than careful observation blood pressure chart uk pdf generic olmesartan 40 mg overnight delivery, even though sensory hallucinations pulse pressure young adults cheap olmesartan 40 mg visa, delirium and behavioral aberrations can be alarming blood pressure upon waking generic 10 mg olmesartan. If manic behavior threatens the safety of the victim blood pressure chart for 14 year old discount olmesartan 10mg line, administer diazepam as a tranquilizer. Phosphine Gas Experience in India suggests that therapy with magnesium sulfate may decrease the likelihood of a fatal outcome. In one series of 90 patients, magnesium sulfate was found to decrease the mortality from 90% to 52%. Because cyanide is so promptly absorbed following ingestion, commence treatment with prompt administration of oxygen and antidotes. The three antidotes - amyl nitrite, sodium nitrite and sodium thiosulfate - are available in cyanide antidote kits, available from various sources. Hydroxycobalamin has been known from animal studies to be an effective antidote for cyanide poisoning. The product became commercially available in 2007 in the United States (Cyanokit, Merck). If more than 50% of total hemoglobin has been converted to methemoglobin, consider blood transfusion or exchange transfusion, because conversion back to normal hemoglobin proceeds slowly. Although various cobalt salts, chelators and organic combinations have shown some promise as antidotes to cyanide, they are not generally available in the United States. None has been shown to surpass the effectiveness of the nitrite-thiosulfate regimen. Severe hemolytic anemia in black children with glucose6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Red Cell Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency-a Newly Recognized Cause of Neonatal Jaundice and Kernicterus in Canada. Observed versus predicted carboxyhemoglobin levels in cellulose triacetate workers exposed to methylene chloride. Pulmonary toxicity following exposure to methylene chloride and its combustion product, phosgene. Acute methyl iodide exposure with delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae: report of a case. Systemic effects of inhalational methyl bromide poisoning: a study of nine cases occupationally exposed due to inadvertent spread during fumigation. Mechanisms involved in cardiac sensitization by volatile anesthetics: general applicability to halogenated hydrocarbons? Outcome of sixty four cases of ethylene dibromide ingestion treated in tertiary care hospital. Mothball withdrawal encephalopathy: case report and review of paradichlorobenzene neurotoxicity. Pulmonary function and bronchial reactivity in asthmatics during low-level formaldehyde exposure. Clinical and laboratory features of acute sulfur dioxide inhalation poisoning: two-year follow-up. Fatalities resulting from sulfuryl fluoride exposure after home fumigation-Virginia. A study of aluminum phosphide (AlP) poisoning with special reference to electrocardiographic changes. Arteriolization of venous blood gases: a clue to the diagnosis of cyanide poisoning. Acute carbon tetrachloride poisoning in 19 patients: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Magnesium status and parenteral magnesium sulphate therapy in acute aluminum phosphide intoxication. Serum & tissue magnesium content in patients of aluminium phosphide poisoning and critical evaluation of high dose magnesium sulphate therapy in reducing mortality. Cyanide antidotes and methods of their administration in dogs: a comparative study.

Ibuprofen is more effective than paracetamol for pain control in ear infection in adults arrhythmia in cats buy olmesartan 20mg visa. Admit and treat approprately if there is fast or difficult breathing blood pressure youtube purchase olmesartan 40 mg free shipping, or if a child is drowsy hypertension medication order olmesartan 40mg without a prescription, has a rash or is very unwell prehypertension young generic olmesartan 10 mg otc. Precaution: Do not give ibuprofen to dehydrated children because it can damage their kidneys. Sinusitis Sinusitis is an infection of the sinus spaces of the front part of skull, most commonly in the maxillary or ethmoid sinuses. As well as symptoms of a viral cold, the person may have pain and tenderness over these sinuses, with a yellow pus discharged. Normally it can be managed with pain control medicine (ibuprofen or paracetamol) alone. When the sinus is very tender or there is a large amount of pus discharge, antibiotics may be needed. Very rarely sinusitis can cause complications such as meningitis or an abscess in the brain. Antibiotics for severe sinusitis Give doxycycline to adults (not to pregnant women), 100mg 1 x day for 7 days or erythromycin 500mg 4 x day for 7 days. It presents a bit like the common cold with runny nose and sore throat but is usually accompanied by high fever, muscle pains, headache and exhaustion. Most symptoms last less than a week, but the cough Hospital and Referral Health Centre Guidelines 61 can continue for two weeks. Complications of flu include a viral pneumonia or secondary bacterial pneumonia, sinusitis and exacerbations of asthma. The treatment is supportive, giving paracetamol and encouraging the person to take more oral fluids. Outbreaks of the Influenza A strain of flu may come in large epidemics, which can be very dangerous depending on the particular sub-strain of virus. Bird flu and pig or swine flu are variants of the influenza A virus that predominantly infect these animals but can also infect humans. Immunisation may become available in the country if there are new epidemics and epidemic control measures put in place. Antiviral medication is expensive, does not help the majority of cases and is not routinely available in the country. Pneumonia and difficult breathing Pneumonia is an infection in the lung, in the lower airway caused mainly by bacteria. The signs of pneumonia are fast and difficult breathing, chest indrawing, cough, fever, sputum. If the child or adult is wheezing then treat for asthma (give antibiotics as well if there is a productive cough and/or signs of consolidation). If available check pulse oximetry and give oxygen by nasal prongs or nasal catheter if oxygen concentration < 95%. Advice: Advise a person treated in outpatients to come back day or night if the child is not improving and the breathing is getting faster. If the person is not rapidly responding to ampicillin and gentamicin, then Ceftriaxone may be needed instead. Amoxicillin should be given (or erythromycin in case of allergy to penicillin) and the person closely monitored. The child does not have pneumonia and should be treated as for the common cold guidelines. If the child has earache or sore throat then the guidelines for ear infection and tonsillitis should also be followed.
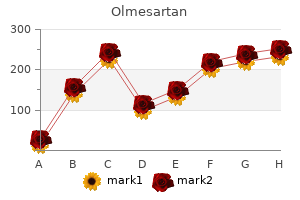
Then there is a slight fall in the middle age blood pressure chart home use generic olmesartan 10mg free shipping, following by a rise after 50 years heart attack is recognized by generic olmesartan 20 mg amex. B symptoms (weight loss fetal arrhythmia 32 weeks buy cheap olmesartan 20mg, night sweats pulse pressure norms 10mg olmesartan, and fever), pruritus, alcohol induced pain, general condition, throat, lymphnodes (site, number, size, consistency, mobility, matting), respiratory system, abdomen (liver, spleen, other masses), bone tenderness. Clinical feature: May first be noticed as a painless swelling of the facial bone or jaw which is typical presentation in equatorial Africa setting. Children with this disease may have some associated anomalies such as: Aniridia, hemihypertrophy, cryptoorchidism and hypospadiasis. Staging: Surgery plays a major role in tumour removal, tumour staging and confirmation of diagnosis as well as visualization of whole abdomen. Clinical features: Manifest according to the site: Abdominal swelling/mass, neurological deficit in case of paravertbral tumours, orbital swelling, and skin lesions. Referral: Urgent referral to a specialized centre Treatment: Combined modality approach: Surgery: Is for early disease or organ preservation. Staging: Localised in the retina vs brain involvement (through optic nerve) Referral: Urgent referral to a specialized centre Treatment: Surgery: Enucleation plus as long a segment of the optic nerve as possible. Treatment: Aim: Cure Surgery: Lesions amenable to wide excision without causing severe functional disabilities are resected. Signs and Symptoms inludes:malaise, fever, fatigue, muscle pain, nausea, anorexia, chill, rigors, sweats, headache, cough, vomiting and diarrhea etc. The above signs and symptoms are not specific for malaria and can be found in other disease conditions. Laboratory investigation is mandatory and urgent for all patients admitted with severe malaria. The exception is in children under 5 years living in high malaria transmission areas, if unable to return for follow up or in case the condition worsens, treat as for uncomplicated malaria. Treatment on the basis of clinical suspicion alone should only be considered if parasitological diagnosis is not accessible. Therefore, an artemisinin alone is the drug of choice as 1st line treatment in the category of neonates and infants below 5Kg, treating as for severe malaria. Injectable quinine remains a suitable alternative where artesunate is not available. Failure to respond to the recommended drug regimen indicates the need for further investigations and appropriate management, with referral if needed. If parasites are found second line treatment should be started and treatment failure recorded. Delay in diagnosis and provision of appropriate treatment may lead to serious complications and even death. In Tanzania the commonest presentations of severe malaria are severe anaemia and coma (cerebral Malaria). Taking and reporting of blood smear must not be allowed to delay treatment unduly. At a health facility the pre-referral dose of parenteral therapy should be initiated without delay. Pre-referral rectal artesunate: Available as suppository containing 50mg or 100mg or 400mg Dosage regimen: Single dose of 10 mg/kg body weight artesunate should be administered rectally. In the event that an artesunate suppository is expelled from the rectum within 30 min of insertion, a second suppository should be inserted and, especially in young children, the buttocks should be held together for 10 min to ensure retention of the rectal dose of artesunate. Table 4: Dosage for initial (pre-referral) treatment using rectal artesunate Weight (Kg) 5-8.
Purchase olmesartan 20mg visa. SmartHeart Automatic Digital Arm Blood Pressure Monitor.
© 2020 Vista Ridge Academy | Powered by Blue Note Web Design